American theoretical physicist Joseph Polchinski once said the existence of magnetic monopoles is ‘one of the safest bets that one can make about physics not yet seen.’ In its quest for these particles, which have a magnetic charge and are predicted by several theories that extend the Standard Model, the MoEDAL (Monopole and Exotics Detector at the LHC) Collaboration has not yet proven Polchinski right, but its latest findings mark a significant stride forward. The new results narrow the search window for these hypothetical particles.
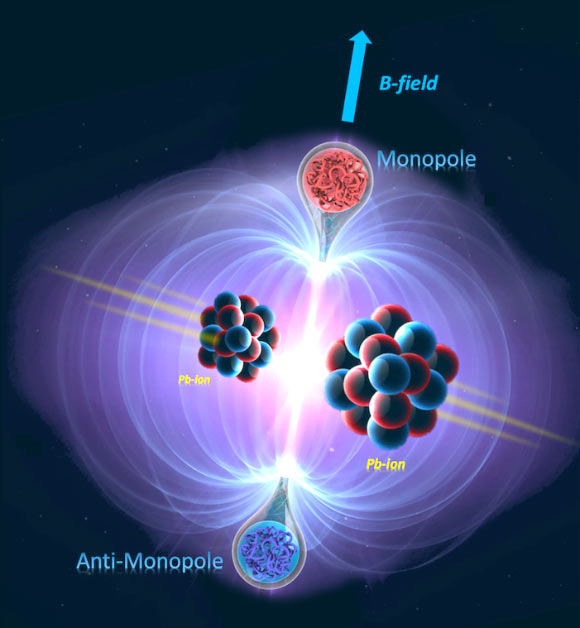
At CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC), pairs of magnetic monopoles could be produced in interactions between protons or heavy ions.
In collisions between protons, they could be formed from a single virtual photon (Drell-Yan mechanism) or the fusion of two virtual photons (photon-fusion mechanism).
Pairs of magnetic monopoles could also be produced from the vacuum in the enormous magnetic fields created in near-miss heavy-ion collisions, through a process called the Schwinger mechanism.
Since it started taking data in 2012, MoEDAL has achieved several firsts, including conducting the first searches at the LHC for magnetic monopoles produced via the photon-fusion mechanism and through the Schwinger mechanism.
In the first of its latest studies, the MoEDAL physicists sought monopoles and high-electric-charge objects (HECOs) produced via the Drell-Yan and photon-fusion mechanisms.
The search was based on proton-proton collision data collected during Run 2 of the LHC, using the full MoEDAL detector for the first time.
The full detector comprises two main systems sensitive to magnetic monopoles, HECOs and other highly ionizing hypothetical particles.
The first can permanently register the tracks of magnetic monopoles and HECOs, with no background signals from Standard Model particles. The second system consists of roughly a tonne of trapping volumes designed to capture magnetic monopoles.
In their latest scanning of the trapping volumes, the researchers found no magnetic monopoles or HECOs, but it set bounds on the mass and production rate of these particles for different values of particle spin, an intrinsic form of angular momentum.
For magnetic monopoles, the mass bounds were set for magnetic charges from 1 to 10 times the fundamental unit of magnetic charge, the Dirac charge (gD), and the existence of monopoles with masses as high as about 3.9 trillion electronvolts (TeV) was excluded.
For HECOs, the mass limits were established for electric charges from 5e to 350e, where e is the electron charge, and the existence of HECOs with masses ranging up to 3.4 TeV was ruled out.
“MoEDAL’s search reach for both monopoles and HECOs allows the collaboration to survey a huge swathe of the theoretical ‘discovery space’ for these hypothetical particles,” said Dr. James Pinfold, spokesperson of the MoEDAL Collaboration.
In their second study, the MoEDAL scientists concentrated on the search for monopoles produced via the Schwinger mechanism in heavy-ion collision data taken during Run 1 of the LHC.
In a unique endeavour, it scanned a decommissioned section of the CMS experiment beam pipe, instead of the MoEDAL detector’s trapping volumes, in search of trapped monopoles.
Once again, the team found no monopoles, but it set the strongest-to-date mass limits on Schwinger monopoles with a charge between 2gD and 45gD, ruling out the existence of monopoles with masses of up to 80 GeV.
“The vital importance of the Schwinger mechanism is that the production of composite monopoles is not suppressed compared to that of elementary ones, as is the case with the Drell-Yan and photon-fusion processes,” Dr. Pinfold.
“Thus, if monopoles are composite particles, this and our previous Schwinger-monopole search may have been the first-ever chances to observe them.”
_____
MoEDAL Collaboration. 2024. Search for Highly-Ionizing Particles in pp Collisions During LHC Run-2 Using the Full MoEDAL Detector. arXiv: 2311.06509
B. Acharya et al. 2024. MoEDAL search in the CMS beam pipe for magnetic monopoles produced via the Schwinger effect. arXiv: 2402.15682